For most tarantula keepers, females are where it’s at.
It’s not that we don’t have love for their male counterparts. In fact, some male species like Phormictopus and Pamphobeteus are more colorful and stunning than the females. No, in most instances, the reason comes down to longevity and their ability to produce young. Female tarantulas are much more long-lived than their male counterparts, often thriving decades after the males have matured and expired. Females can also be bred to produce slings, an integral and fascinating part of the hobby for many.
The story is a bit different for male tarantulas. Some species of male tarantulas can mature in just over a year, leaving you with a leggy, antsy boy who wanders around his enclosure in a desperate attempt to fulfill his life’s goal to mate with a willing female. At this point, the best thing you can do for this tarantula that you have lovingly raised and cared for is to ship him off to someone with a female for breeding, leaving you with an empty cage. Sure, you can do do a breeding trade for half of the slings a successful pairing produces, but not all attempts end in viable sacks, and some end with the male being unceremoniously munched.
Those who enjoy raising tarantulas (and who don’t feel like paying the higher prices for sexed females) will often pick up spiderlings. As small slings are often difficult, if not impossible, to sex accurately, you never know exactly what you’re getting when you pick up a tiny spiderling. Many keepers (myself included) will pick up three or more slings of the same species at a time to increase their chances of getting a female. You then feed them, love them, and watch for signs that you might have hit the spider jackpot with a female.
Sometimes you notice one growing faster than the others, and immediately suspect a male. After all, males in many species will grow and mature faster. Other times, you see the spider’s underside pressed up against the side of its enclosure and you swear you see female parts. And still others, you’ll latch on to some physically dimorphic feature, like color or patterning, in hopes that it indicates a female.
Any keeper who has patiently waited to sex a spider they have raised from the sling stage has undoubtedly experienced the thrill of discovering they have raised a young lady … or the letdown that their beloved pet is a more short-lived male.
How do you sex a tarantula?
There are several methods keepers to use to determine the sex of their tarantulas, but many are not very accurate or require the keeper to have plenty of experience as well as a keen understanding of the anatomy of many species.
One method used to sex tarantulas is ventral sexing, which entails examining the tarantula’s ventral area (the bottom of the tarantula) around the epigastric furrow to try to determine its gender. The epigastric furrow is an opening between the set of book lungs closest to the cephalothorax (body) of the spider. Folks using this method will compare the curve of the furrow, the distance between the anterior book lungs, and the angle of the lungs to determine gender.
In females of some species, the epigastric furrow is more pronounced with what can be described as “lips”. In others, it is not nearly as pronounced. This method takes plenty of practice and knowledge of what both the female and male characteristics of each species are. Keepers attempting this technique will want to do some research and get some photos of both males and females for comparison.
Personally, I don’t even try to sex via ventral shots anymore, as I don’t feel that I’m particularly good at it, and it’s often not very accurate. Sure, some species like some of the Poecilotheria sport some fairly obvious lady parts early on, but others can be quite misleading and difficult to determine. Arachnoboards has a wonderful area where keepers can post ventral shots of their Ts so that others can determine the sex, but due to the trickiness of using this technique, many of the responses are just guesses (as evidenced by the same spiders being proven to be a different sex later on). Still, if you attempt this method, try posting a good ventral photo up on this board to get some other opinions.
There is also the epiandrous fusillae method. With this technique, the keeper looks for epiandrous fusillae, or a second set of micro spinnerets used by mature male tarantulas to create sperm webs. This is a technique that requires a keen eye and a lot of practice, so it might not be the most appropriate for some keepers, especially those new to the hobby.
Sexing your spider using the molt
The best way to your tarantula is to examine its exuvia or molted exoskeleton. An intact molt from a larger specimen (smaller specimens may require use of a microscope) can be examined for evidence of the female’s spermathecae, or the receptacle the female that stores the male’s sperm in. This organ is often described as a little “flap” or “pouch” above the epigastic furrow.
Although this method can be tricky at first, especially with smaller specimens, it’s the most accurate and easy to practice. All you need is an intact molt, some good lighting, and you can give it a shot. Here’s how to go about it:

A comparison of molts from a 3.5″ male and a 3.5″ female T. stirmi. The piece of paper on the female molt is showing the “flap”.
1. First off, you’ll want to do some research and find reference photos for both a male and female of the species you want to sex. I would encourage folks to hop on Arachnoboards’ Tarantula Sexing board and check out some of the shots there, or do a Google or Bing image search and study some of those. Every species is different, so looking at a molt from a L. parahybana might not be useful for determining the sex of a GBB.
2. Next, you need a molt that has the abdomen flesh containing the book lungs intact. If the abdomen has been completely shredded in this area, you will find it difficult or impossible to sex the molt. I try to grab the molts from spiders I want to sex right after they molt (as long as I can do it without disturbing the tarantula).
3. You need to soften up the exuvia, or molt, to make it less fragile and more pliable. I use a very small spray bottle and give it a few squirts. I then wait a few minutes for the molt to soften up. Other folks will drop the molt into a dish of warm water for a minute or so. Either of these methods work, just use care when handling the molt not to tear it or get urticating hairs on you. You may also want to put it on a piece of paper towel to wick up some of the excess water.
4. Position the molt so that the fangs are facing up and the molt is on its “back” on your well-lit working area. I like to use white plates myself, but a piece of foam board would be great if you want to pin the molt down. Now, carefully spread out the legs and unfurl the abdominal skin if it has become twisted. Work slowly and carefully, as the area that you need to sex the molt is VERY fragile and will tear. I will usually use toothpicks and cotton swaps to unfurl mine. You want to open up this abdominal skin so that you can see the underside of the area where the two sets of book lungs are.
5. Now, some folks will immediately spot a slit between the set of book lungs closest to the body and think that they have a girl. Not so. This slit is found on both males and females. What you are looking for is a pronounced “flap” or the spermathecae, which will be above the epigastic furrow if present. The smaller the specimen, the more difficult this area can be to see. I often use a magnifying glass or take a close-up photo with my phone to get a better look. On well-developed females, you can even take a small piece of paper and slide it behind the flap to be sure.
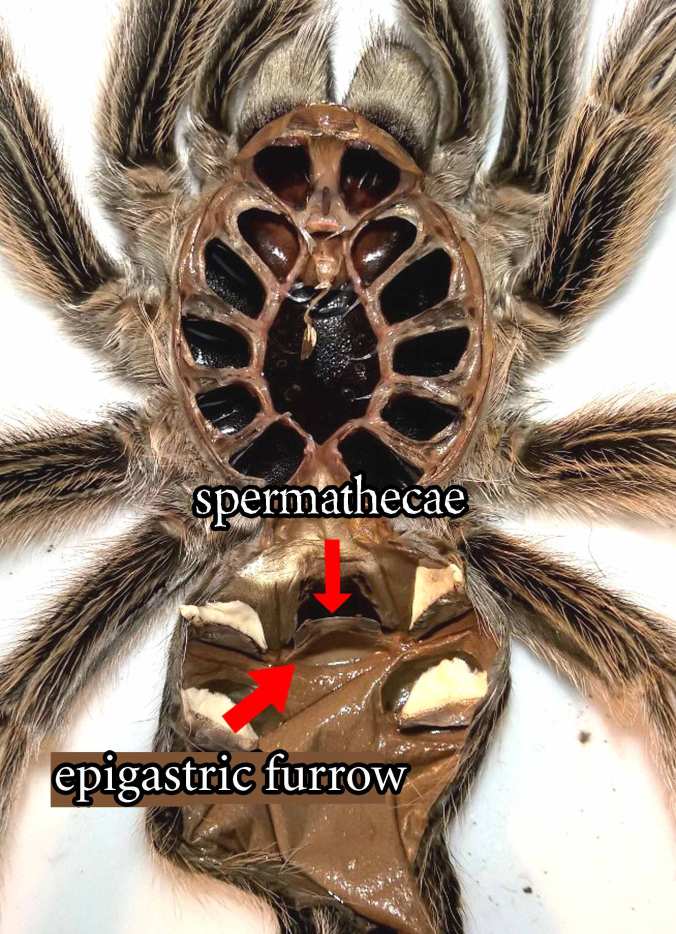

If you find the spermathecae, congratulations … it’s a girl! If not, and you are sexing a largerer specimen, you are likely looking at a male. You can always try again on a future molt to double-check.
Now this all sounds quite simple, but it’s not always that cut and dry. Some species don’t develop enough for the casual keeper to sex until later in their life cycles. Also, males from some species will have organs that can be mistaken for spermathecae, meaning that sexing those species can be a bit more challenging. If you are trying to sex your pet, you should spend some time researching and examining molt photos from both the males and females of the species. For some wonderful reference diagrams of the spermathecae of females from different species, check out this site. A Google search will also bring up several useful photos, and you can also check the sexing topic on Arachnoboards and compare the photos.
Recognizing mature males
It should be mentioned that mature males can be quite easy to sex, and you will often hear keepers refer to their males as “hooking out.” This expression comes from the fact that males from some species develop tibial “hooks” behind the knees of their first set of walking legs upon maturing. The key word here is “some”, as many species will not present this feature while others, like some in the Avicularia genus, will have hooks too small to see.
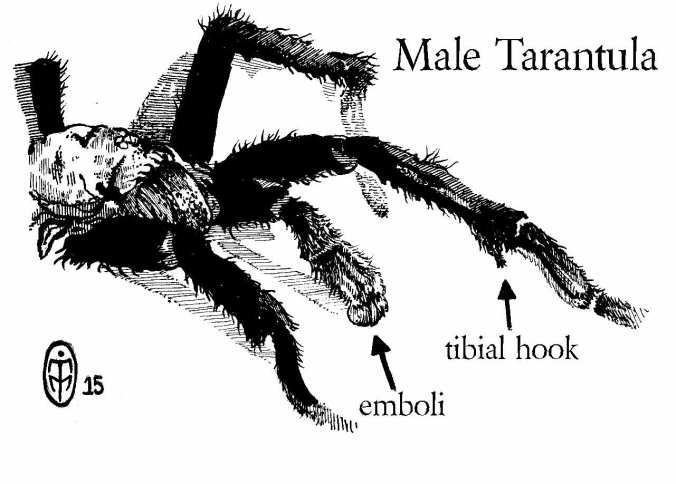
An illustration of a male tarantula. Some species don’t have tibial hooks, so it is better and more accurate to look for the emboli.
Honestly, the phrase should be changed to “bulbing out” or something similar, as keepers should be keeping an eye out for another telltale feature; namely the bulb-like emboli at the end of the male pedipalps. The pedipalps are the shorter set of appendages inside the first set of walking legs that look like shorter legs. When a male spider has his ultimate molt, he develops emboli, or essentially the male’s sexual organ used to deliver the sperm to the female, on the end of his pedipalps. Instead of the ends of these appendages looking like the rest of the tarantula’s “feet”, they will instead be round and bulbous (some keepers refer to them as “boxing” gloves).
Because all male tarantulas will develop this feature, it makes more sense to look for emboli when trying to determine if your spider is a mature male or not.
Not only do males mature much faster than their female counterparts, but there are often many physical differences between a male and female of the same species. First off, males tend to be thinner and “leggier” than the girls, who are much more heavy-bodies. Many male tarantulas have different colorations than females, with some being very pronounced. Female L. violceopes, for example, sport gorgeous iridescent blues and purples upon reaching maturity. Males, on the other hand, are brownish to olive in color. Some males also mature at a much smaller size than the females of the same species; this can lead to some confusion for keepers who discover that their gangly male is done growing at 5″ and will never reach the 7″ max size of the females they’ve read about.
Unfortunately, many of these features won’t appear until the specimen’s ultimate molt, so those using this “method” would literally be discovering their pet’s sex at the latest possible opportunity.
Lots of practice is required!
No matter what method you choose to try to sex your specimen, research and practice are key. I have literally examined over a hundred molts now and spent countless hours staring at sexed molts on my computer screen. And although I feel like I’ve definitely got the hang of it, I still have difficulties at times. I’m certainly not yet an expert yet. When you’re first starting out, be sure to try and sex every molt you can. Do you have specimens that are already sexed male or female? If so, examine and photograph their molts as practice and to use as references.
With all of the variations between species, it can be very difficult to know what to look for. I would encourage anyone attempting to sex their T to look up the species first and find out all you can about it’s anatomy or any sexual dimorphism. Some questions you should be researching are:
Are their differences in colorations, marking, or bandings between the sexes?
Is this a species that can be sexed ventrally with accuracy?
What is the shape of the female’s spermathecae?
At what size to the genders become apparent enough to accurately sex by molt?
Does the male of this species have an organ that could be mistaken for a spermathecae?
Does the male of this species have tibal hooks?
Sexing may seem daunting and confusing at first, but with enough practice, most keepers will be successfully identifying the genders of larger specimens in no time. And honestly, the first time you examine a molt and discovering that the sling you have raised for a year is a little lady makes all of the effort and frustration worth it.
* Note: I will continue to update this blog with photos of sexed molts. It’s my hope that this can be a resource for some looking for reference photos.






Yep all that is awesome…unless your T chomps on the exuvia. I’m having conniptions over a couple of mine refusing to let me in on the little secret because of that. 😀
LikeLike
Oh, man…I hear you. I have two GBBs that used to shred EVERY molt. I FINALLY got a complete shed from one recently. Soooo frustrating!
LikeLiked by 1 person
My A. avic, my P. ornata are the main culprits. The ornata I can “color” sex (tentatively) as female as her carapace and abdomen striping patterns are consistent with the female, and my A.a posed for a really good ventral shot…which LOOKS female. (not holding my breath on either.) I actually don’t care if the sex is male or female though. I like the hobby for the experience as well as the variety. Plus next year (almost certainly), my very first two purchases (Dorian and Tiphane, the G. porteris) will become bestest of friends as Dorian is an immature male at nearly 5″ and Tiphane is most definitely a mature female. heh.
LikeLike
This may not be pertinent to the article exactly, as it has nothing to do with sexing… but to do with the molt: has anyone ever noticed, upon examining the freshly molted exoskeleton, that some of the hairs, particularly nearer the tips of the legs, continue to twitch for a while??
LikeLiked by 1 person
Hi, Claire!
I’m going to have to keep an eye out for that now. I’ve never noticed the twitching! 🙂
Tom
LikeLike
Hello, Tom! Though it’s deemed hard, is it at all possible to tell a sling’s gender? Or do they only start to deviate in appearance when they reach maturity? My 1.25 inch C. versicolor is looking very leggy. This is my first spider, though, so it’s not as though I’ve had another to compare with. Thanks!
LikeLike
Ty bro is so helpfull
LikeLike
You’re most welcome!
LikeLike